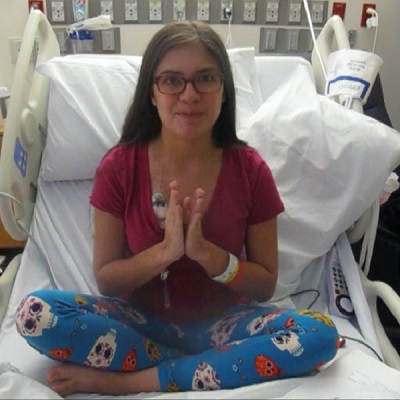
Lung cancer is one of the most common and serious types of cancer. Around 22,000 new cases of lung cancer are recorded every year in Vietnam. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it’s also the leading cause of death from cancer.
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer occurs when cells in the lung grow abnormally out of control and form tumors. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. Smoking causes the majority of lung cancer cases. Early stages of lung cancer may not produce symptoms; however, early diagnosis and treatment is important to ensure the best outcome. Lung cancer may be treated with surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Causes
Smoking is the most common cause of lung cancer. Cancer occurs when cells grow abnormally and out of control, instead of dividing in an orderly manner. Exposure to second-hand smoke, polluted air or water, and certain industrial chemicals increases the risk for lung cancer. However, people that have never smoked may also develop lung cancer.
There are different types of lung cancer that are categorized as:
-
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) - most common type. NSCLC tends to grow and spread slowly.
-
small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
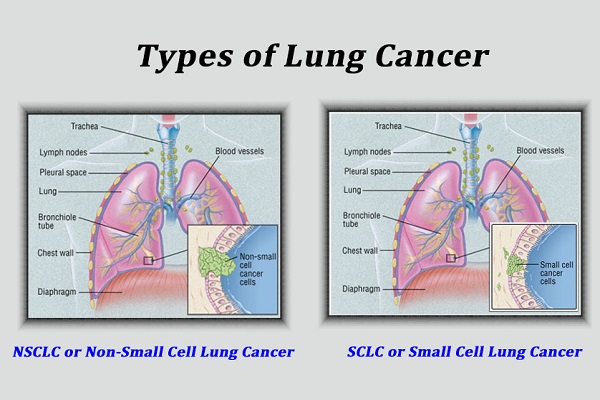
1. Three forms of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are:
- Adenocarcinomas- NSCLC: are generally located in the outer portion of the lung.
- Squamous Cell Carcinomas- NSCLC: generally originate in the center of the lung by a bronchus.
- Large Cell Carcinomas- NSCLC: can occur in any part of the lung. They are the fastest growing and spreading type of NSCLC
2. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is the fastest growing type of lung cancer. SCLC can be very aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body, such as the brain, liver, and bones. SCLC can cause large tumors. The most common type of SCLC is oat cell cancer, which is named for the shape of the cancer cells. SCLC may also be categorized as mixed small cell/large cell carcinoma or combined small cell carcinoma. Smoking is almost always the cause of SCLC.
Lung cancer may not cause symptoms or may cause only minimal symptoms in the early stages. Symptoms of lung cancer include a new cough that will not go away or worsening of a chronic cough, such as a smoker’s cough. You may cough up blood and/or develop pneumonia and bronchitis repeatedly. You may experience changes in the way you breathe, such as wheezing and shortness of breath. You may have chest pain. You may lose your appetite and lose weight without trying. You may feel tired all of the time. Less common signs include swallowing problems, a hoarse voice, back pain, joint pain, weakness, and facial swelling, drooping, or paralysis.
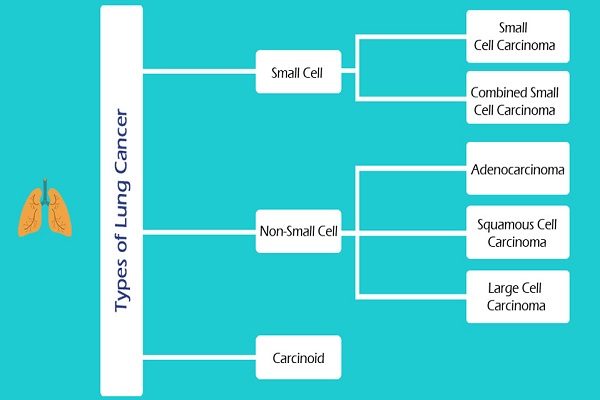
Stages of non-small cell lung cancer
- Stage I: The cancer is located only in the lungs and has not spread to any lymph nodes.
- Stage II: The cancer is in the lung and nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage III: Cancer is found in the lung and in the lymph nodes in the middle of the chest, also described as locally advanced disease. Stage III has two subtypes:
- If the cancer has spread only to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest where the cancer started, it is called stage IIIA.
- If the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes on the opposite side of the chest, or above the collar bone, it is called stage IIIB.
- Stage IV: This is the most advanced stage of lung cancer, and is also described as advanced disease. This is when the cancer has spread to both lungs, to fluid in the area around the lungs, or to another part of the body, such as the liver or other organs.
Complications
Lung cancer can spread to other parts of the body, including the other lung, brain, bones, lymph nodes, and liver. Some types of lung cancer are aggressive and can spread quickly. Lung cancer may recur or come back after it has been treated. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in Vietnam.
The CDC says the best way to reduce your risk of lung cancer is to not smoke and to avoid secondhand smoke. Screening is not a substitute for quitting smoking.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can begin to diagnose lung cancer by reviewing your medical history and conducting a physical examination and some tests. You should tell your doctor if you smoke or if you have ever smoked. Your doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope while you breathe. You may perform breathing or pulmonary tests to assess how your lungs are functioning. Your sputum may be tested for infection.
Chest X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and computerized tomography (CT) scans are used to provide images of your lungs to help diagnose cancer. A bronchoscopy may be used to view the inside of your lungs. This test involves inserting a thin fiberoptic tube through your windpipe (trachea) and into your lungs. A thoracoscopy is used to examine the lining inside and outside of your lungs. A biopsy may be taken of tissue or fluids to examine the cells for cancer. A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis and identify the type of lung cancer.
If you have lung cancer, your doctor will assign your cancer a classification stage based on the results of all of your tests. Staging describes the cancer and how it has metastasized. Cancer that has spread from its original site to other parts of the body is termed metastatic cancer. Staging is helpful for treatment planning and recovery prediction.
There is more than one type of staging system for cancer, and you should make sure that you and your doctor are referring to the same one. Generally, lower numbers in a classification system indicate a less serious cancer, and higher numbers indicate a more serious cancer. The stages may be subdivided into classifications that use letters and numbers.
Prevention
Smoking causes most cases of lung cancer. You may prevent cancer by not smoking or quit smoking. If it is difficult for you to quit smoking on your own, ask your doctor about medications and resources to help you. You should avoid exposure to second-hand smoke.
You should have your home or business checked for radon gas. Radon gas rises from the soil beneath a home and may enter it through cracked foundation, pipes, or other openings. You cannot see or smell radon, and the only way to know if it is present is to have a specific test for it. Radon gas levels may be corrected if they are high.
Make sure that you are following safe working practices if you are exposed to asbestos, uranium, arsenic, and certain petroleum products at your job. Workers that smoke and are exposed to such chemicals have a greater risk of developing lung cancer.
Am I at risk?
Risk factors may increase your likelihood of developing lung cancer, although some people that develop lung cancer do not have any risk factors. People with all of the risk factors may never develop the disease; however, the chance of developing lung cancer increases with the more risk factors you have. You should tell your doctor about your risk factors and discuss your concerns.
Risk factors for lung cancer:
- Cigarette smoking causes the majority of lung cancer. Smoking pipe tobacco or cigars also can contribute to lung cancer. However, people that have never smoked may develop lung cancer.
- Inhaling second-hand smoke from others increases your risk of lung cancer.
- Exposure to high levels of air pollution increases the risk of lung cancer.
- High levels of arsenic in drinking water are associated with lung cancer.
- Radon gas in homes or businesses can cause lung cancer.
- You have a greater risk for lung cancer if your family members have had lung cancer.
- Lung scarring from chronic emphysema, bronchitis, and other conditions can raise the risk of lung cancer.
- Exposure at your job to cancer-causing substances, such as asbestos, uranium, arsenic, and certain petroleum products, increases the risk of developing lung cancer. People that are exposed to such products and smoke have even a greater risk.
- Radiation therapy to the lungs can increase the risk of lung cancer.
Screening for Lung Diseases and Cancer
For more information on lung cancer screening, visit: https://cih.com.vn/en/internal-surgical-medicine/1797-lung-cancer-screening-and-prevention.html
Check out our different Screening Packages for different needs
For appointment or screening service consultation, please contact:
- Ms. Võ Thị Mỹ Liên: (8428) 6280 3333, ext. 8424
- Ms. Nguyễn Thị Lệ: (8428) 6280 3333, ext. 8402
For appointment or more information about the services provided, please contact City International Hospital
- Operator: (8428) 6280 3333, ext. 0
- Address: Level 3, No. 3, 17A Street, Binh Tri Dong B Ward, Binh Tan Dist. (Next to AEON Mall Binh Tan). Ho Chi Minh City.
- Website: https://cih.com.vn/en/